|
|
Seismic Hazard and Dam Safety
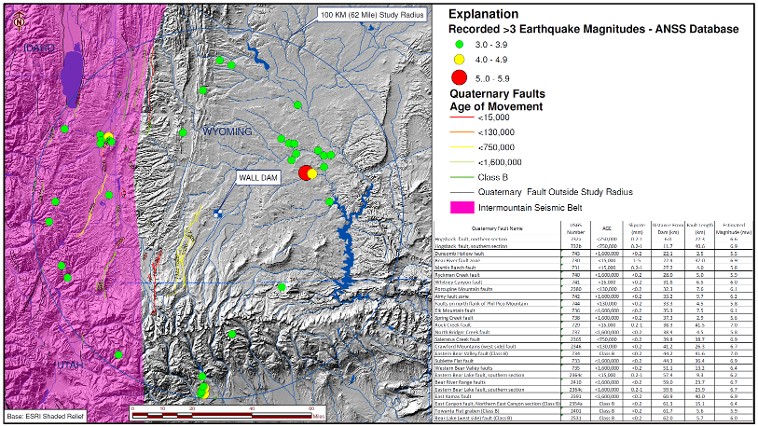 Seismic hazard analysis, Austin-Wall Dam, Uinta County, Wyoming Seismic hazard analysis, Austin-Wall Dam, Uinta County, Wyoming
Geologic
and Geoseismic Support, Austin-Wall Dam Level II Study, Fort Bridger, Uinta County
Wyoming - Senior Geologist 2010-2011. Support
included engineering geology mapping, geological hazards characterization,
using photogeologic analyses of site imagery, GIS analyses of elevation and
terrain data, and reconnaissance to the site.
Seismic hazard characterization was also conducted to evaluate the
Maximum Credible Earthquake (MCE) and the Operating Basis Earthquake (OBE) for
the dam site. Also supervised field
drilling activities for the geotechnical engineer. |
Seismic
Hazard Assessment, Weber Basin Water Conservancy District. Davis, Weber and Box Elder Counties, Utah –
Project Geologist, 2009. Performed a seismic hazard assessment for
District System, primarily using GIS for assessment. Hazards assessed included, general geology, strong ground motion
(both peak horizontal acceleration and modified Merchalli), exposure of the
system to surface fault rupture hazards, liquefaction potential, landsliding,
and debris flows hazards. |

Forebay drilling, Ashton Dam, Ashton Idaho
|
Geotechnical
and Geophysical Field and Laboratory Services, PacifiCorp Ashton Dam; Ashton,
Idaho - Project Manager, 2005. In support of the Civil Engineer (Black
& Veatch) performed piezometer testing, ground penetrating radar (GPR)
Survey, geotechnical drilling and sampling, and laboratory testing services to
support the Civil Engineer to perform seepage investigation.
Geotechnical
and Geological Feasibility Evaluation, Proposed Spring Creek Reservoir; Uintah
County, Utah - Project Geologist, 2003. Feasibility evaluation of the proposed dam
site was conducted to evaluate the site relative to performance as a dam site,
exposure to seismic and geological hazards, suitability of soil and rock materials
on the site for use in dam construction, and recommendations as to dam
structure. Surface and subsurface
investigation included excavation of 20 test pits and three rock-core borings
to as much as 290 feet. During the rock-core drilling, Packer testing was
conducted to evaluate the hydraulic conductivity of the rock units underlying
the dam and reservoir. Our findings were used by the County for the decision as
to proceed with or abandon the site for proposed dam construction. |
Geoseismic
Evaluation, PacifiCorp Klamath River Hydroelectric Project - Project Manager,
2008. The Klamath Hydroelectric Projects
consists of the J.C. Boyle Dam in Klamath County, Oregon, and the Copco No. 1
and Iron Gate Dams in Siskyou County, California. Because the dams are
undergoing studies for Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)
re-licensing, the FERC requested that seismic studies to be conducted that
addresses the capability of regional earthquake faults, including the West
Klamath Lake Fault Zone, the Cedar Mountain fault system and the Cascadia Subduction
Zone. To characterize the seismicity of the dams, a regional seismic
survey supported with GIS was performed consistent with the Federal Guidelines
for Dam Safety, which include probabilistic earthquake parameters as well as
calculating the Maximum Credible Earthquake (MCE) and the Operating Basis
Earthquake (OBE) for the dam sites. |
PacifiCorp Cove Pond
Sediment Characterization Study; Caribou County, Idaho - Project Manager, 2005. The Cove
Pond is an approximately 1200-foot long by 400-foot wide reservoir on the Bear
River that is impounded by a 27-foot high dam that redirects water into a flume
for hydroelectric generation. The dam has impounded water in the reservoir
since 1912, and sediments from upstream areas have been captured behind the
dam. Because significant agricultural,
industrial, waste disposal and mining activities occur up-stream of the
reservoir, the potential for the accumulation of hazardous levels of chemical
constituents in the captured sediments aren a concern. The Client was considering
the decommissioning of the Cove Pond Dam as part Federal Energy Regulatory
Commission (FERC) re-licensing requirements. The action would involve removing
the dam, and the sediments behind the dam could potentially migrate down
stream. Because of the concerns regarding the chemical constituents that may be
contained within sediments behind the Dam, the Idaho Division of Environmental
Quality (DEQ) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has requested
that these sediments be analyzed for hazardous constituents that may have
become concentrated behind the dam. To characterize the sediments, we sampled
the pond sediments using, a barge mounted geo-probe sampler over the Cove Pond
water surface. The sampled sediments were tested for constituents specified by
the Idaho DEQ and EPA, and were found not have hazardous levels of chemical
constituents requiring remedial actions. |

Barge mounted geoprobe, Cove Pond, Caribou County, Idaho

Downstream butress drilling, Austin-Wall Dam, Uinta County, Wyoming
|
|
|